You might wonder, ‘who could need such a long list of foods with vitamin D, and why?’ Can’t blame you. Others might ask that same question and also find it extensive. Perhaps that’s why so many have this nutritional deficiency.
Surprisingly, many people, even those that live on a sunny beach, have a deficiency. Despite warmly tanned skin, they are shocked to learn they aren’t receiving enough.
What’s even more curious is that I wasn’t alone. It was shocking to learn that nearly half of the population is also deficient in vitamin D!
If you suspect or already know you’re in the same boat as that population, consider adding a few foods to boost your vitamin D level. Don’t worry; there are plenty of options to choose from! You won’t have to revamp your diet to address this deficiency.
31 FOODS THAT FUEL YOUR BODY WITH VITAMIN D
1. Swordfish
Each day, children and adults should aim for 600 IU, or international units. Interestingly enough, very few foods are naturally packed with vitamin D. The good news for seafood lovers is that fatty fish can provide you with some of the highest vitamin D levels.
Swordfish, in particular, is packed full of the ‘happy vitamin.’ You can get over 560 IU of your daily vitamin D from just one serving.
That means that just a single vitamin D-packed portion would come just shy of fulfilling your daily value!
2. Yogurt
It is critical to ensure you get your daily dose of the ‘sunshine vitamin.’ You can avoid typical vitamin D deficiency symptoms like backaches, depression, and chronic fatigue. Allowing your body to stay deficient in D vitamins for too long can lead to more serious ailments like high blood pressure and diabetes!
Including yogurt fortified with vitamin D as a regular part of your diet can fuel you with up to 71 IU of your daily dosage. Don’t worry about trying to find fortified yogurt. In today’s world, you must search hard to find unfortified yogurt.
The reason behind this is a good one. As time passes, more and more children and adults are proving to have a deficiency in this essential vitamin. One way to address this is through fortifying affordable foods that are widely eaten.
Let’s not forget–this stuff is also an excellent source of calcium.
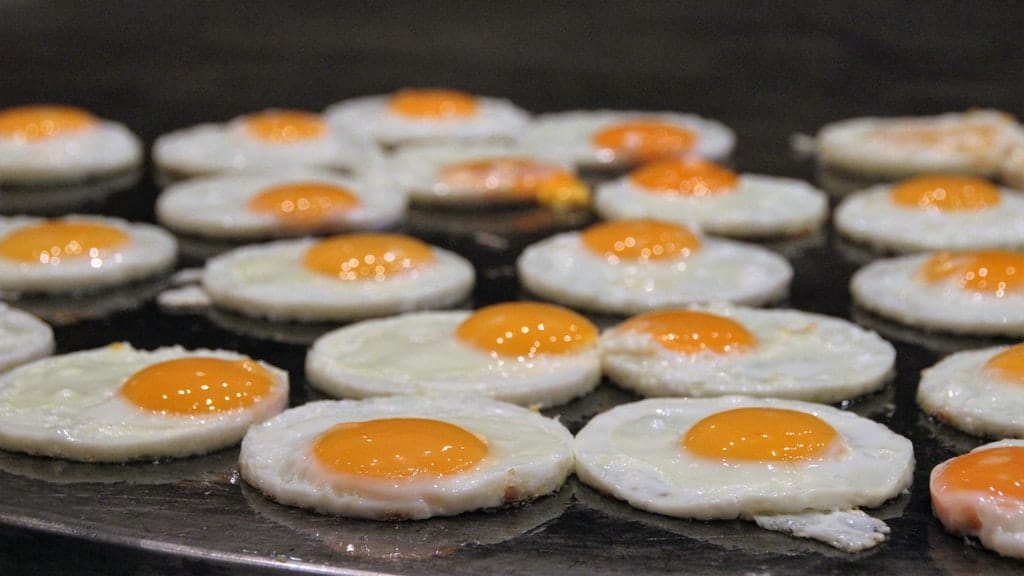
3. Egg Yolks
It’s important to note that not everyone can easily absorb vitamins D2 and D3 through natural sunlight. For those with a darker complexion, the melanin in their skin can negatively impact the absorption rate of D vitamins.
Did you know they don’t see sunlight in parts of Alaska for over two months? It’s a wonder that the entire state isn’t deficient when they are void of sunshine for over 60 days a year!
If you’re concerned about your absorption level, you may consider adding eggs to your breakfast a few days a week. A single egg contains about 33 IU of your daily goal. Starting the day with a couple of eggs and a bowl of oatmeal sounds like the perfect way to start the day.
4. Portobello Mushrooms
Mushrooms are a curious source of the ‘sunshine vitamin,’ considering they grow in the dark. As it turns out, when grown naturally, most mushrooms provide an insignificant amount of vitamin D2 and D3. However, the moment they are exposed to UV light, they become packed with these vitamins.
Portabella mushrooms are a breed of fungus that can also provide you with a bit of vitamin D4. All in all, a cup of these tasty morsels packs a whopping 634 IU. That exceeds the recommended allowance all by itself!
5. Cod Liver Oil
Living in Alaska and having more melanin aren’t the only factors that can cause you to be deficient in D vitamins. Those living with liver and kidney diseases, Crohn’s disease, or osteoporosis are also at a higher risk of being inadequate.
Many add cod liver oil to their regimen for other health benefits like reduced inflammation and stronger bones. But did you realize that cod liver oil is also a great source of your D vitamins? A single teaspoon is loaded with 427 IU.
6. Cow’s Milk
Unfortunately, infants are another group who struggles to absorb the proper amount of the ‘sunshine vitamin.’ This is even truer if the mother lacks this essential nutrient, as she provides sustenance. Fortunately, a fortified formula can help if this becomes an issue.
Once the child is old enough, fortified milk becomes one of their primary sources of D vitamins. Do you remember learning that most yogurts are fortified?
That is true with nearly every dairy product in several countries. This ensures that children and adults can quickly and cheaply receive the necessary calcium and vitamins. Each cup of milk holds approximately 100 IU with this measure in place.
7. Oysters
Recall that there aren’t many foods that are rich in D vitamins. While oysters possess some of this vitamin, they are pretty low on how much they provide.
Still, people add them on occasion from time to time for a bit of variety. Oysters are particularly beneficial to those looking for a boost in zinc. After all, they are the number one source of this mineral.
The funny thing about oysters is that their shell carries more of vitamins. Many supplements that address calcium and vitamin D deficiencies contain the oyster shell.
8. Pacific Mackerel
Not only is pacific mackerel delicious, but it also has over 340 IU of your daily ‘happy vitamins.’ In addition to having one of the highest IU, it’s also an excellent source of omega-three fatty acids.
Research shows that omega-three fatty acids greatly benefit heart health and reduce inflammation.
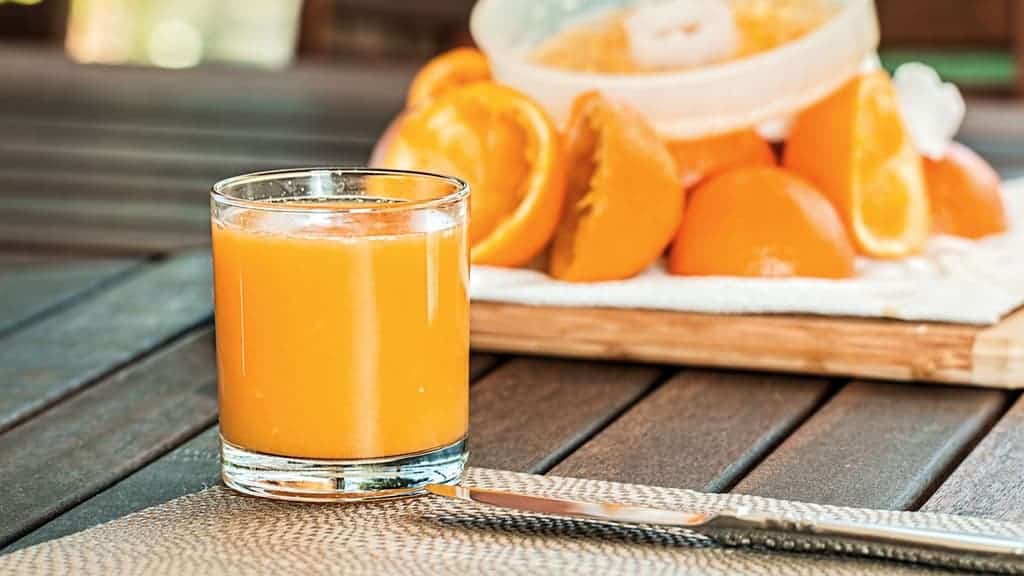
9. Orange Juice
Some people falsely believe it would be impossible for a vegan to reach their daily intake of D vitamins. However, that isn’t the case with UV technology and fortification processes.
Remember that, unlike dairy products, not all orange juice is fortified. If you choose a fortified juice, you can get about 100 IU daily dose this way.
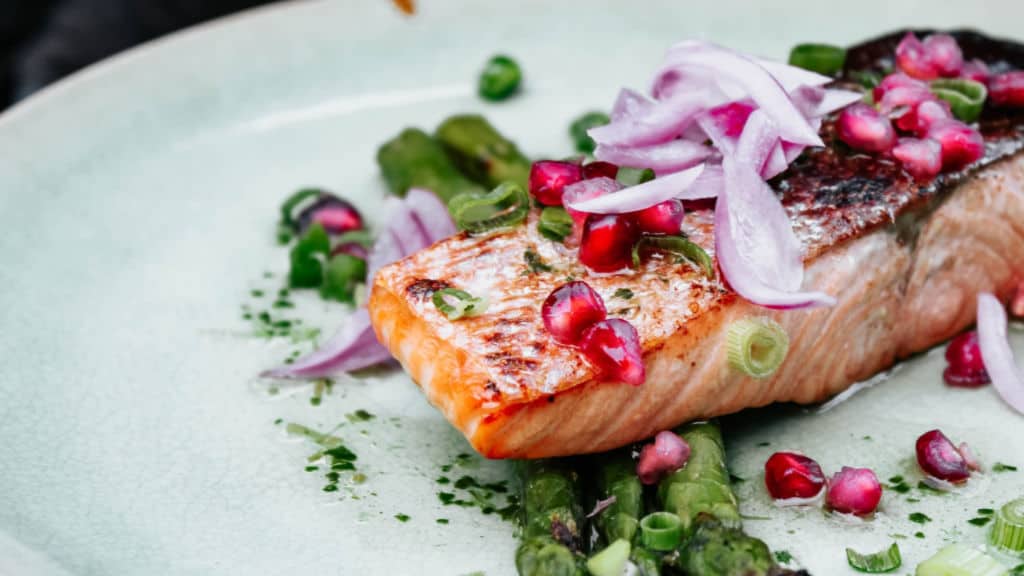
10. Salmon
Salmon is another one of those foods with multiple health benefits. Because of its omega 3’s, when included as a regular part of the diet, it’s proven beneficial in relieving asthma symptoms.
It’s just a bonus that it’s a great source of D vitamins, providing between 205 and 385 IU, dependent upon the variety.
11. Beef Liver
A serving of liver can provide you with approximately 40 IU, so it falls a bit low on the scale of foods rich in D vitamins. However, that’s still enough to make an impact.
Aside from providing D vitamins, it’s also a good source of protein, iron, zinc, copper, and vitamins A and B12.
12. Pork
It is already widely known that the composition of lean pork is very similar to red meat. Studies are currently underway to determine just how similar they are. Researchers have found evidence to suggest that occasionally eating lean pork can improve cardiovascular issues.
Lean cuts of pork can also assist you in reaching your daily intake of D vitamins. Depending on the cut, you could consume up to 60 IU when eating this flavorful meat.
13. Tuna
Tuna is one of the tastiest and most commonly eaten D vitamin-rich food. Considering the 60 IU, you can find in a single can of tuna. It’s no wonder so many people love it! Fresh albacore tuna is even denser in vitamins, providing around 100 IU.
If that weren’t enough motivation to eat more tuna, consider how vital it is to maintain proper brain function. DHA is a fatty acid found only in breast milk and certain fish, like tuna.
When eating fish, you mustn’t overindulge. Some fish contain high levels of mercury, and yellowfin tuna certainly falls into this category.
Fatty fish is essential in your diet, but you want to monitor how much mercury you ingest. Switch it up occasionally and choose a fish with lower mercury levels.
14. Margarine
Margarine is yet another fortified food. It’s such an essential source of D vitamins for children that it has become one of the leading sources in the United Kingdom.
Just one teaspoon delivers about 30 IU. Try cooking dinner with margarine or adding a bit to your toast to finish the day off.
15. Soy Milk
Fortified soy milk can be a terrific alternative for those with milk allergies or prefer not to eat animal products. Soy milk is the only plant-based milk comparable to cow’s milk in regards to key vitamins and nutrients.
Thanks to fortification, soy milk can provide you with the same protein, calcium, and D vitamins as cow’s milk.
16. Ice Cream
Okay, so maybe ice cream is more of a sweet treat than a substantial source of D vitamins. But you don’t have to feel guilty about giving in to your sweet tooth occasionally.
Since it’s made of fortified dairy products, even this sweet dessert will give you 1% of your daily intake. There’s a silver lining, after all, albeit it is a skinny one.
17. Sardines
By now, you’re well aware that varying types of fish are packed with omega 3s and D vitamins. Sardines are no exception to the rule. Whether you have them on a pizza or out of a can, you can absorb an impressive 144 IU when eating this food.
Did you know that regularly including fatty fish in your diet can considerably decrease your risk for diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s?
18. Maitake Mushrooms
Here’s a fun fact for you: maitake mushrooms are a superfood. Sure, every cup is packed with 780 IU of D vitamins, but that fails compared to its superpower.
These mushrooms are so powerful that they can help fight off a viral infection. Oh, did I mention that they’ve also been shown to decrease the activity in cancer cells?!
19. Almond Milk
Almond milk is a good alternative if you’re trying to overcome this deficiency but still mindful of your fat and carbohydrate intake. It’s also low in calories. So, the only actual downside is that it doesn’t have nearly as much protein as cow’s milk.
Even the level of D vitamins is comparable, weighing in at 85 IU per cup.
20. Herring
What a surprise, yet another fatty fish has made it into the lineup. Is it any wonder when you know that fish makes up the largest category of foods with vitamin D?
Just a single serving of Atlantic herring can provide you with 200 IU of your daily value. Stopping by the fish market this weekend is sounding like a better and better idea.
21. Chanterelle Mushrooms
Regarding mushrooms, chanterelle mushrooms fall pretty low on the totem pole. However, with over 100 IU of D vitamins to offer, they are certain qualifiers amongst foods with vitamin D.
What makes them even more worthy of being added to your diet is that they possess significant healing and anti-inflammatory characteristics.
22. Sturgeon
Sturgeon is a white meat fish known to be a delicacy in several countries worldwide. It’s most famous for its caviar, or its eggs.
When eating the meat of this fish, you can expect to consume just over 430 IU of D vitamins per serving. Even the caviar contains 70 IU.
23. Roe
Roe is slightly higher in D vitamins than caviar, weighing in at 145 IU per serving. Fish roe has additional benefits, particularly for those who have noticed crow’s feet starting to creep up. You may have guessed by now that fish roe is praised for its anti-aging and antioxidant characterizations.
24. Soy Yogurt
Soy yogurt is an ideal dairy-free alternative, as it’s also low in fat. However, it has more in common with regular yogurt than you may expect. It still has all of your essential amino acids and probiotics.
In addition, it has the same amount of ‘sunshine vitamins’ as the regular version–a great way to overcome a deficiency.
25. Trout
Like a handful of other fish, Trout can provide up to 200 IU of your daily dose of D vitamins. Not to mention, it’s high in protein and low in carbs. It’s also a far less fatty fish than a few others mentioned here.
26. White Mushrooms
White mushrooms are unique in that both sun exposure and UV exposure will cause their amount of vitamin D to jump significantly. When these mushrooms grow in the dark, they only contain 7 IU, but that skyrockets to 1200 IU when exposed to light!
27. Halibut
Halibut and trout are very similar in their nutritional makeup. They are both low in fat, and you’ll notice there are no carbohydrates found when eating halibut. However, halibut has slightly fewer D vitamins, at only 144 IU.
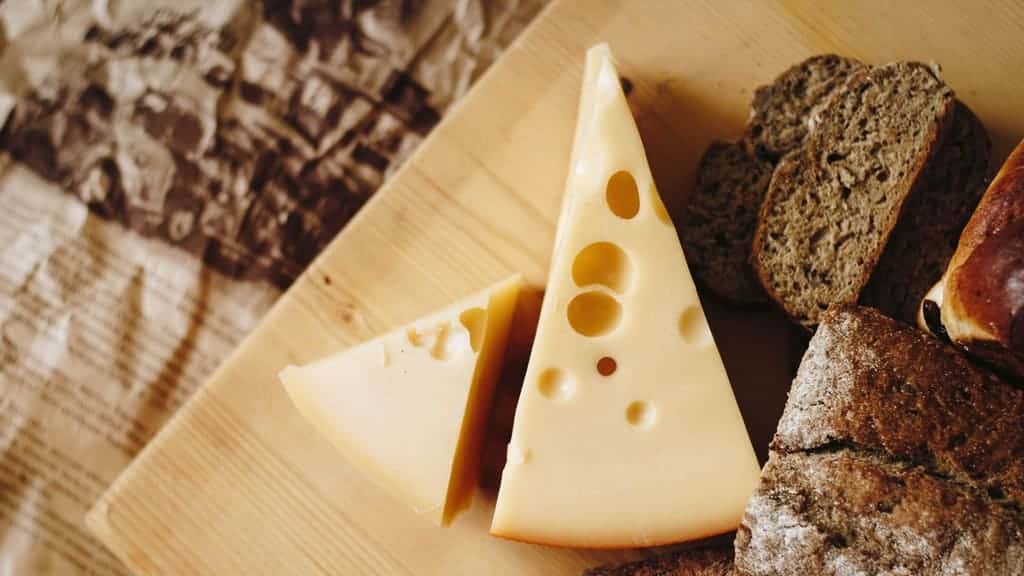
28. Cheddar Cheese
Cheddar cheese may not be the first thing that comes to mind when considering foods with vitamin D. Justifiably, a single slice of cheddar cheese will only provide you with 7 IU.
However, it’s important to remember that D vitamins are not the only vitamins or minerals you want to keep in mind. While cheddar cheese doesn’t rank exceptionally high in this field, it ranks highly in calcium-rich foods.
Whether it is through cheese or fish, you want to keep a variety in your meals. If you overeat cheddar cheese or certain types of fish, you would consume too much fat.
29. Fortified Breakfast Cereal
What’s more convenient, first thing in the morning, than pouring a bowl of cereal? I can’t think of many things with a shorter kitchen preparation time.
Next time you’re picking up cereal, consider choosing oat bran that’s fortified with vitamin D. Key things you want to look for are “whole grains” and “low sugar content.”
Remember that checking the nutritional label when browsing any fortified goods is essential. Just because it’s high in specific vitamins and minerals doesn’t mean it isn’t packed full of excess sugars and fats!
30. Goat Milk
Goat milk is another option that is available for individuals with milk allergies. Over recent years, its popularity has increased partially due to its wide popularity in Mediterranean countries.
However, the driving reason behind this rise in popularity is that dairy products made from goat milk are affordable. There have also been a rising number of people with allergies to cow’s milk who may not react to goat milk.
Aside from containing the same D vitamins as cow’s milk, goat milk is also a good source of protein, calcium, and potassium. After learning all of that, it’s a bonus to find that it also has significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory attributes.
31. Swiss Cheese
A serving of Swiss cheese has slightly fewer D vitamins than cheddar cheese, with only 6 IU. While you can get a small amount of your daily intake from swiss cheese, your vitamin K level will greatly benefit you when eating this snack.
There are three types of swiss cheeses that have varying levels of Vitamin K12. At 433 ng/g, Emmenthal has the most significant amount. Alternatively, Gruyere will only provide you with just over 60 ng.
Final Thoughts on Adding Vitamin D to Your Diet
With over 40% of the world’s population with a vitamin D deficiency, the time to be more intentional with our eating has arrived.
If you have children, ensuring they consume the proper amount of D vitamins is crucial. Since children have a skeleton that has not yet developed, a vitamin D deficiency could cause a bone disorder called rickets.
Fortunately, it is easier now than ever to find foods with vitamin D. There once was a time, not too long ago, where fish was the primary source.
Now, through fortification processes, regulations, and UV photosynthesis, there are more options than we could have ever imagined.
Along with children, vegans and vegetarians struggled to meet their daily intake of the ‘happy vitamin.’ Products like fortified soy, almond milk, and fortified breakfast cereals can address this common deficiency.
If you, like many in our population, face a variety of food allergies, there’s hope for you too. With supplements being made of various products ranging from certain mushrooms to oyster shells, there’s an avenue available for us all to avoid a vitamin D deficiency.





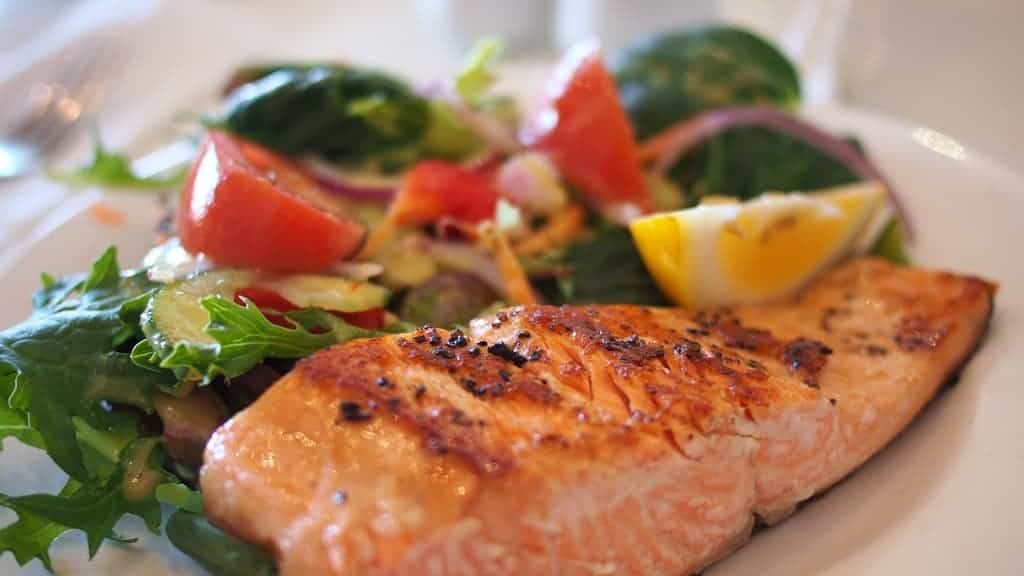












 Community
Community

