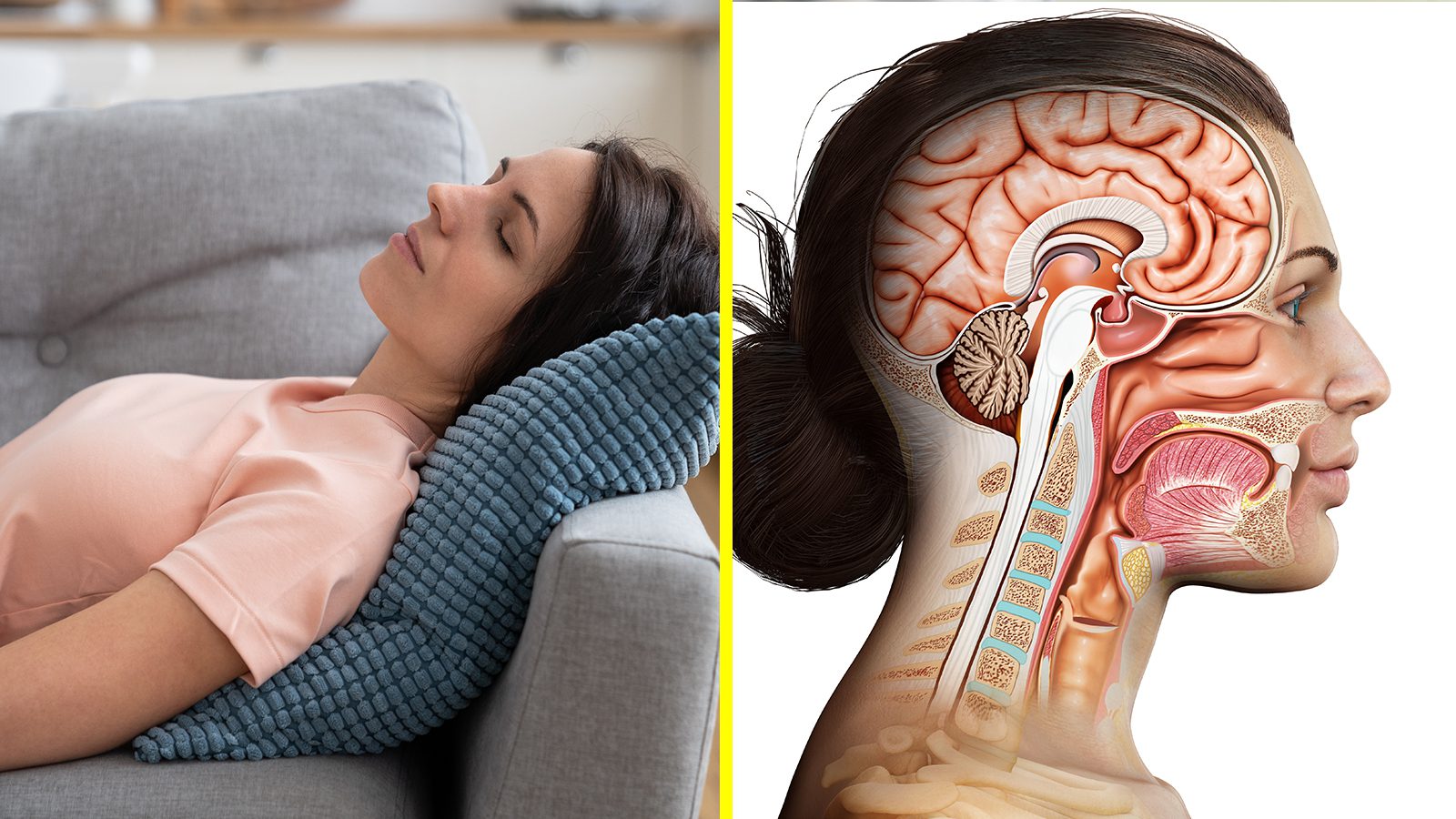
If you enjoy napping regularly, you’ll be pleased to know the delightful habit has numerous benefits for your brain. Some might think taking naps is lazy. But certain countries, such as Spain, revere the practice. It’s nice to take a break from difficult mental or physical labor and relax your mind. Our minds and bodies weren’t meant for long hours of labor without rest; napping can give us a short reprieve. And it turns out – it’s great for our brain health.
Scientists from the University College London confirm this with a new study, finding that naps are linked to increased brain volume. Therefore, taking siestas can reduce your risk of developing dementia and enhance cognitive functioning as you age. Even young people can benefit from naps, but the study only included adults aged 40 to 69. Below, we’ll discuss the research that discovered how frequent naps positively impact brain health.
Understanding Napping
In the modern world, the power nap has become increasingly popular in recent years. Daytime sleep offers a short respite from the demands of daily life and allows the brain to recharge. A short sleep period during the day plays a significant role in cultures worldwide, such as in Spain and parts of Latin America. Other Mediterranean countries like Italy and Greece also indulge in naps due to the warm climate and cultural traditions.
The Western world slowly accepts this idea because of the fast-paced culture and stressful modern jobs. Napping helps rejuvenate the brain, increases productivity and creativity, and reduces work-related stress. While some bosses still view naps at work as a waste of time, others have embraced the idea and encourage workers to rest during breaks.
The Science of Sleep
Sleep profoundly impacts the brain and body, helping remove waste products from brain cells and regulate metabolism. It also increases brain plasticity, improves memory, and enhances the immune system. Without quality sleep, the body and mind become susceptible to various illnesses such as depression, diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.
Each night, the brain goes through four sleep stages: one for rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and three for non-REM sleep. The first two stages include N1 and N2, or light sleep, which occur in the first 30 minutes of sleep. N3, or deep sleep, follows these stages and lasts 20 to 40 minutes. Finally, the brain falls into REM sleep, where vivid dreams and memory consolidation occur. REM sleep usually lasts for 10 to 60 minutes per cycle, increasing in duration throughout the night. Most healthy adults experience four to six sleep cycles per night.
Research on Napping and Brain Health
Now that you know the importance of the various sleep cycles, we’ll discuss recent research on how napping affects brain health. Researchers from the University College and London and the University of the Republic in Uruguay performed the study on napping benefits. Their brain health research discovered that short daytime naps in adults aged 40 to 69 led to better cognitive functioning and reduced dementia risk. They also had a larger total brain volume, which can slow aging by 2.5 to 6.5 years.
The research confirms the results of previous sleep studies, which showed that short rest periods increase cognitive performance on tests. However, the current study didn’t discover any differences in other markers of brain health, such as visual processing, reaction time, and hippocampus volume.
Sleep and Memory Retention
Research shows that napping can improve brain functions like memory, learning, and alertness in older adults. Naps enhance cognitive function by rejuvenating the brain’s energy and eliminating waste products from cells. They improve short-term memory because they help clear the brain of information overload and allow it to recharge. In addition, napping helps long-term memory in adolescents and older adults because the slow brain waves that occur in light sleep increase neuroplasticity.
Napping and Neurological Diseases
Numerous studies have shown that high-quality sleep can help reduce the risk of neurodegenerative illnesses like Alzheimer’s and dementia. Daytime naps can offset the harmful effects of sleep deprivation, which may help older adults with insomnia. People with Parkinson’s disease may also find 10 to 30 minute daytime naps helpful in reducing fatigue associated with the illness.
Since poor sleep quality increases brain inflammation and amyloid plaques, it’s a significant risk factor for developing Alzheimer’s. Therefore, getting as much restorative deep sleep as possible can protect the brain from age-related cognitive decline. People with Parkinson’s disease may also find daytime naps helpful in reducing fatigue associated with the illness.
How to Nap Effectively
You may wonder about the optimal nap length to ensure the best brain health benefits. It will differ depending on your lifestyle and needs, but most experts say 30 minutes to one hour is sufficient. A nap should help you feel rejuvenated and ready to return to work, but not groggy or exhausted. Therefore, the optimal napping time for most people is 30 minutes or less to provide the most significant cognitive benefits. However, older adults may find a longer rest helps them feel more refreshed and alert. To follow sleep hygiene guidelines, take naps in the early afternoon to avoid disrupting your sleep schedule.
Other Health Benefits of Napping
Regular naps also benefit your physical health by reducing blood pressure and promoting cardiovascular function. In addition, a siesta can positively impact your psychological health by increasing serotonin and dopamine, making you feel relaxed and happy. Finally, hitting the hay in the afternoon can help with stress management since you’ll get a short break from work or school, allowing you to decompress.
Final Thoughts on Napping and Brain Health
Scientific research on napping shows that daytime rest can improve brain functioning and reduce stress levels. A 30 to 60-minute nap helps remove toxic waste products from the brain, increasing memory, learning, and concentration capability. Other benefits of napping for brain health include reduced risk of developing Alzheimer’s and dementia because it increases brain volume. In addition, studies show that getting daytime beauty sleep can positively impact heart health and mood. To practice a healthy lifestyle, consider taking a daily siesta for better emotional, mental, and physical wellness.