We need a certain amount of various nutrients daily; vitamins and minerals, in particular, are crucial elements to nearly every critical biological process in the human body. Given how much food the average American consumes, it’s astonishing to think that we’d have any problem acquiring the appropriate nutrients. However, we do have several nutritional deficiencies that are strangely common.
“Nutrient deficiencies alter bodily functions and processes at the most basic cellular level.” ~ Tricia L. Psota, Ph.D., RDN
Don’t Overlook Deficiencies of These Essential Nutrients
1. Iron Deficiency
Iron is the main component of red blood cells. It binds to the substance hemoglobin and transports oxygen throughout the body.
There are two dietary varieties of iron: heme and non-heme. Heme iron is easily absorbed and is mainly found in animal foods, especially red meat. However, non-heme iron is more common. You can find it in both animal and plant foods. However, your body does not absorb it as readily as heme iron.
The World Health Organization (WHO) advises that this deficiency causes anemia, a blood disease. They estimate that iron deficiency is the most widespread nutritional hurdle in the world, impacting:
- 33% of non-pregnant women
- 40% of pregnant women
- 42% of children worldwide
Symptoms of iron deficiency include impaired cognitive function, impaired immune system function, fatigue, and a weakened immune system.
The best sources of heme iron include the following items: red meat, seafood, organ meat, and canned sardines. The best sources of non-heme iron include kidney beans, pumpkin, sesame, or squash seeds, broccoli, kale, and spinach.
2. Vitamin D Deficiencies
Vitamin D is critical for skin and bone health and nerve transmission throughout the body. Exposure to sunlight is paramount to natural Vitamin D acquisition, as the vitamin is created from cholesterol produced by the skin.
Vitamin D is the “sunshine vitamin” because the most potent source is spending time outdoors in the sunshine. However, that leaves people in cloudy regions apt to miss out on sufficient exposure.
One scientific article estimates that an average of 50% of people fails to get sufficient Vitamin D globally. This estimate includes the following:
“In the United States, 47% of African American infants and 56% of Caucasian infants have vitamin D deficiency, while over 90% of infants in Iran, Turkey, and India have vitamin D deficiency. In the adult population, 35% of adults in the United States are vitamin D deficient whereas over 80% of adults in Pakistan, India, and Bangladesh are Vitamin D deficient, in the United States, 61% of the elderly population is vitamin D deficient whereas 90% in Turkey, 96% in India, 72% in Pakistan, and 67% in Iran were vitamin D deficient.”
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency include these symptoms: fatigue, muscle aches, and weakness. The symptoms of vitamin D deficiency can be vague, however.
Besides the sunshine, the food sources of vitamin D include these items: fortified milk or yogurt, fatty fish (mackerel, salmon, trout), cod liver oil, and egg yolks. It is tough to get enough vitamin D from diet alone, so exposure to sunshine daily is essential.
3. Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B-12 is critical for proper brain and nerve function and the production of DNA. Per Harvard Health Publishing, vegetarians and vegans, in particular, may be at risk for developing B-12 deficiency as plants do not produce the nutrient.
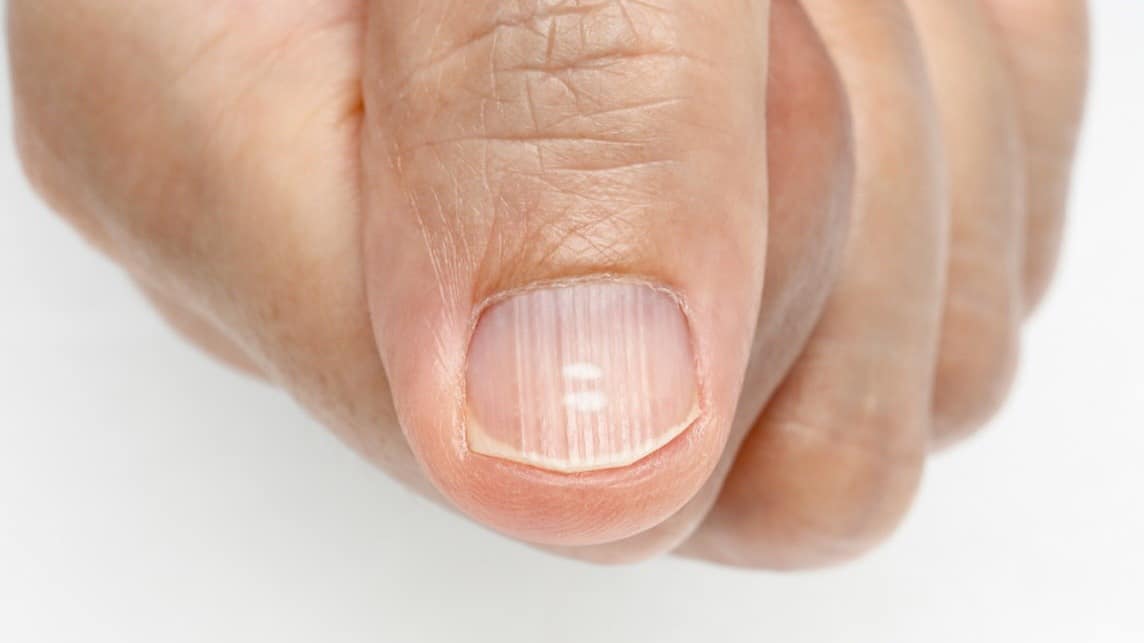
Symptoms of B-12 deficiency may include numbness in the feet, hands, or legs; dizziness, weakness, fatigue; a swollen, inflamed tongue; memory loss, paranoia, and hallucinations. In addition, a 2018 article in BMJ Case Reports cites a lack of B-12 as the cause of hyperpigmentation of the fingernails.
The following people tend to lack this vitamin, according to science: 80 to 90% of vegetarians, 20% of older adults, and around 30% of U.S. adults.
The best sources of B12 include fish, chicken, milk, and yogurt. Besides, the best sources for vegans include nutritional yeast, meat substitutes, and fortified soy or almond milk.
4. Calcium Deficiency
Calcium, as we all know, is crucial to bone health and maintenance. But calcium is also essential to nerve transmission. Indeed, without it, our primary organs would not be able to function correctly.
Calcium deficiency estimates: 80 to 90% of vegans and vegetarians; 20% of elderly individuals. And 30 to 40% of U.S. adults.
Symptoms of calcium deficiency include abnormal muscle heart rhythm, bone fragility, and muscle cramps. The best sources of calcium include whole milk and dairy products, dark green vegetables, and boned fish.
5. Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium is a critical mineral that affects just about every bodily function. ‘Mg’ is crucial for brain function, nerve signaling, bone structure, and enzymatic reactions.
It is estimated that up to half of the U.S. population consumes the required amount of magnesium. Magnesium deficiency can contribute to several diseases, including heart disease, osteoporosis, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and muscle weakness.
Good sources of magnesium include nuts (almonds and cashews), whole grains, dark chocolate, and dark leafy green vegetables.
6. Folate Deficiency
Folate is a B vitamin that is naturally present in many foods. A form of folate called folic acid is used in certain dietary supplements and fortified foods. Folate plays a crucial role in the manufacturing and producing DNA and other genetic material. Besides that, your body requires it for cell division and synthesis.
Symptoms of folate deficiency include fatigue, mouth sores, and changes in the color of hair, weak or brittle fingernails, and dry or flaky skin. Excellent sources of folate include beans, fortified cereals, dark leafy greens, and lentils.
7. Iodine Deficiency
Iodine is an essential mineral for normal thyroid function and the production of thyroid hormones. Furthermore, it is vital for brain development, bone health and maintenance, metabolic regulation, and growth.
Iodine deficiency is one of the most common nutritional deficits in the world. In fact, a German study monitored iodine and found about 33% of participants to have low levels. Iodine deficiency may produce many symptoms, including increased heart rate, enlarged thyroid gland (goiter), trouble breathing and shortness of breath, and weight gain.
So what are the best sources of iodine? Try to include shellfish, seaweed, white fish, dairy, and eggs in your diet.
















 Community
Community

